Day 15: Start a New Yancy App

Yancy is a new content management plugin for the Mojolicious web framework. Yancy allows you to easily administrate your site’s content just by describing it using JSON Schema. Yancy supports multiple backends, so your site's content can be in Postgres, MySQL, and DBIx::Class.
Demonstration
For an demonstration application, let’s create a simple blog using Mojolicious::Lite. First we need to create a database schema for our blog posts. Let's use Mojo::Pg and its migrations feature to create a table called "blog" with fields for an ID, a title, a date, some markdown, and some HTML.
# myapp.pl
use Mojolicious::Lite;
use Mojo::Pg;
my $pg = Mojo::Pg->new( 'postgres://localhost/blog' );
$pg->migrations->from_data->migrate;
__DATA__
@@ migrations
-- 1 up
CREATE TABLE blog (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
title VARCHAR NOT NULL,
created TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT NOW(),
markdown TEXT NOT NULL,
html TEXT NOT NULL
);
-- 1 down
DROP TABLE blog;
Next we add the Yancy plugin and tell it about our backend and data. Yancy deals with data as a set of schemas which contain items. For a relational database like Postgres, a schema is a table, and an item is a row in that table.
Yancy uses a JSON schema to describe each item. For our blog
schema, we have five fields:
idwhich is an auto-generated integer and should be read-onlytitlewhich is a free-form string which is requiredcreatedwhich is an ISO8601 date/time string, auto-generatedmarkdownwhich is a required Markdown-formatted stringhtml, a string which holds the rendered Markdown and is also required
Here's our configured Yancy blog schema:
plugin Yancy => {
backend => 'pg://localhost/blog',
schema => {
blog => {
required => [ 'title', 'markdown', 'html' ],
properties => {
id => {
type => 'integer',
readOnly => 1,
},
title => {
type => 'string',
},
created => {
type => 'string',
format => 'date-time',
readOnly => 1,
},
markdown => {
type => 'string',
format => 'markdown',
'x-html-field' => 'html',
},
html => {
type => 'string',
},
},
},
},
};
Yancy will build us a rich form for our schema from the field types
we tell it. Some fields, like the markdown field, take additional
configuration: x-html-field tells the Markdown field where to save the
rendered HTML. There's plenty of customization options in the Yancy
configuration documentation.
Now we can start up our app and go to http://127.0.0.1:3000/yancy to manage our site's content:
$ perl myapp.pl daemon
Server available at http://127.0.0.1:3000
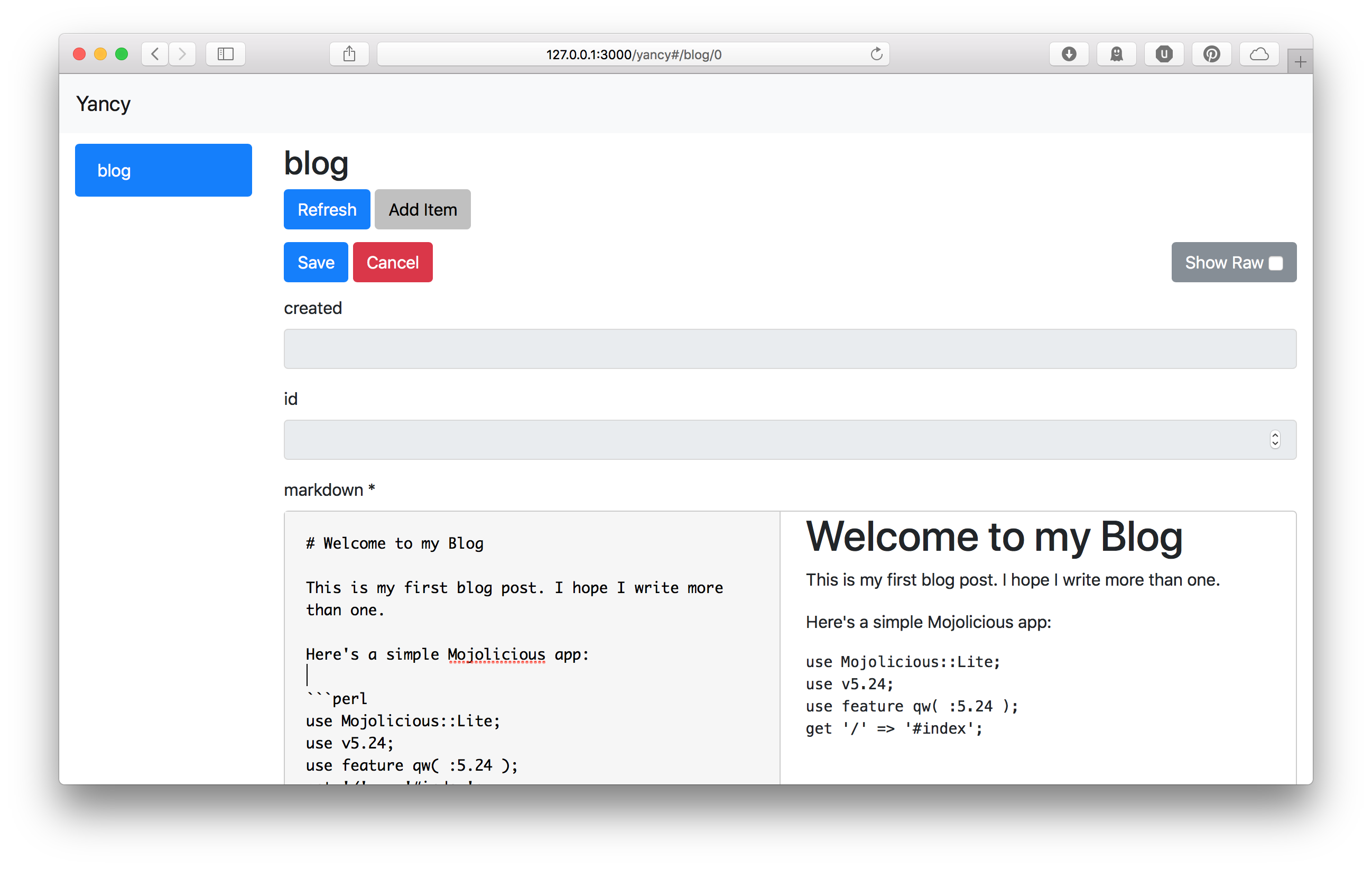
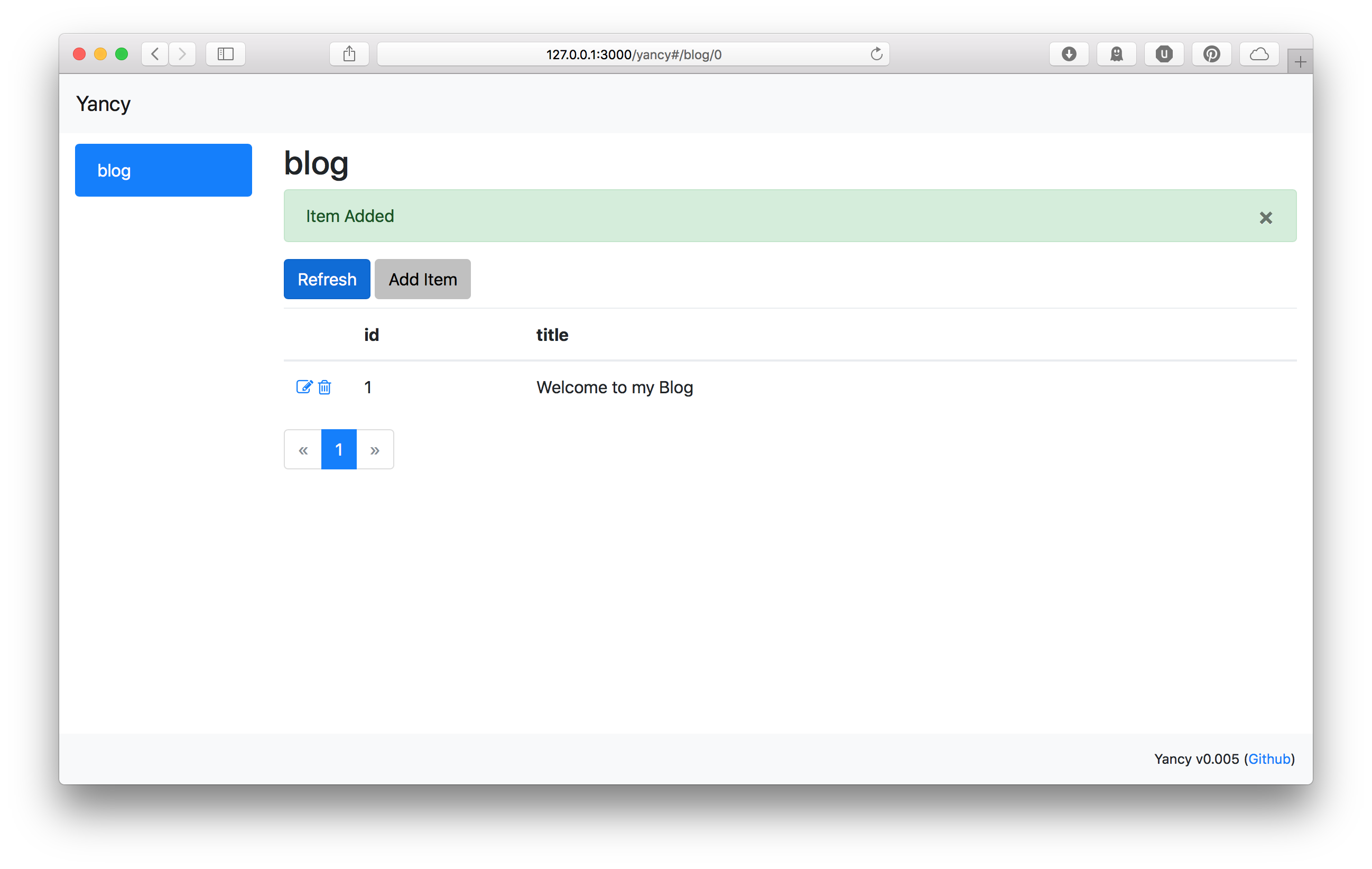
Finally, we need some way to display our blog posts. Yancy provides
helpers to access our
data. Let's
use the list helper to display a list of blog posts. This helper takes
a schema name and gives us a list of items in that schema. It
also allows us to search for items and order them to our liking. Since
we've got a blog, we will order by the creation date, descending.
get '/' => sub {
my ( $c ) = @_;
return $c->render(
'index',
posts => [ $c->yancy->list(
'blog', {}, { order_by => { -desc => 'created' } },
) ],
);
};
Now we just need an HTML template to go with our route! Here, I use the standard Bootstrap 4 starter template and add this short loop to render our blog posts:
<main role="main" class="container">
% for my $post ( @{ stash 'posts' } ) {
<%== $post->{html} %>
% }
</main>
Now we have our completed application and we can test to see our blog post:
$ perl myapp.pl daemon
Server available at http://127.0.0.1:3000
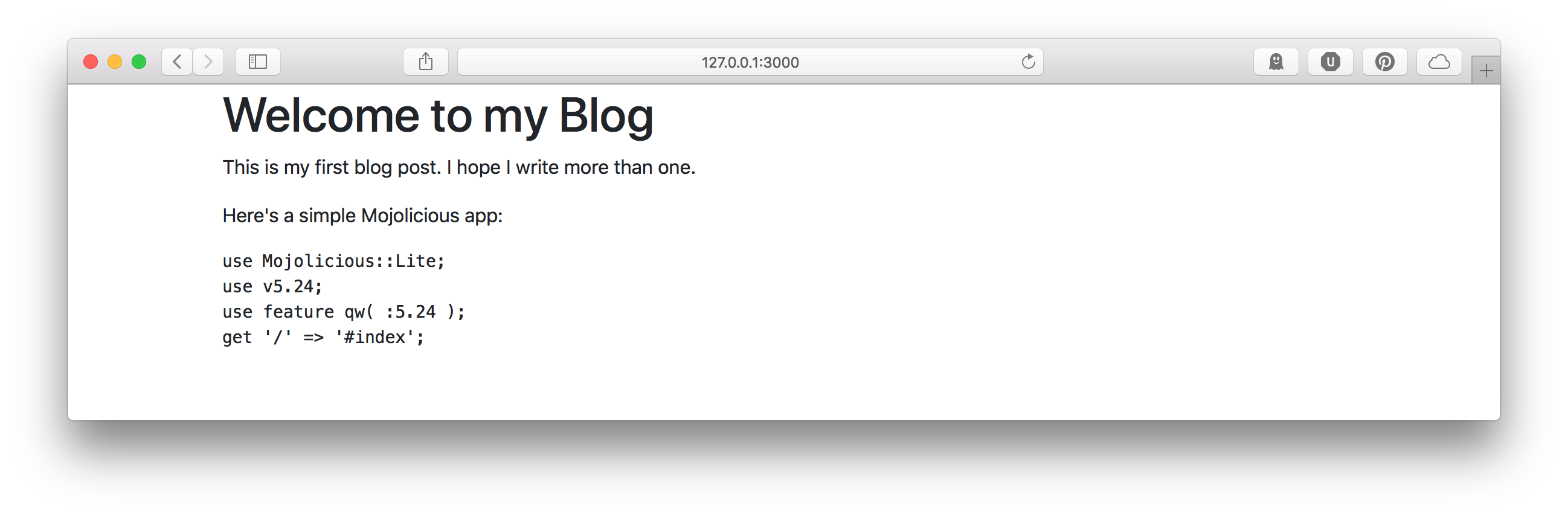
Yancy provides a rapid way to get started building a Mojolicious application (above Mojolicious’s already rapid development). Yancy provides a basic level of content management so site developers can focus on what makes their site unique.
Image in the public domain.
Doug Bell
Doug (preaction) is a long time Perl user. He is the current maintainer of CPAN Testers and the author of many CPAN modules including the Statocles blog engine that powers this site.